Image source: Wikimedia Commons
Welcome to our article on food safety and the 7 principles of HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points).
In this guide, we will explore the crucial aspects of HACCP and how it ensures safe consumption and handling practices in the food industry.
With these principles, businesses can significantly reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses, promoting a healthier and safer environment.
Key Takeaways:
- HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is essential for food safety in the industry.
- By adhering to the 7 principles of HACCP, businesses can ensure safe consumption and handling practices.
- Implementing HACCP requires proper training, auditing, and following best practices.
- HACCP principles contribute to reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses and promoting a healthier environment.
Understanding HACCP and Its Importance in Food Safety
In today’s globalized and fast-paced world, ensuring food safety is of paramount importance. One highly effective tool that plays a crucial role in maintaining food safety standards is HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points).
HACCP is a systematic approach to identifying and managing potential hazards throughout the food production process. By implementing a HACCP system, food establishments can proactively prevent incidents of contamination and minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses.
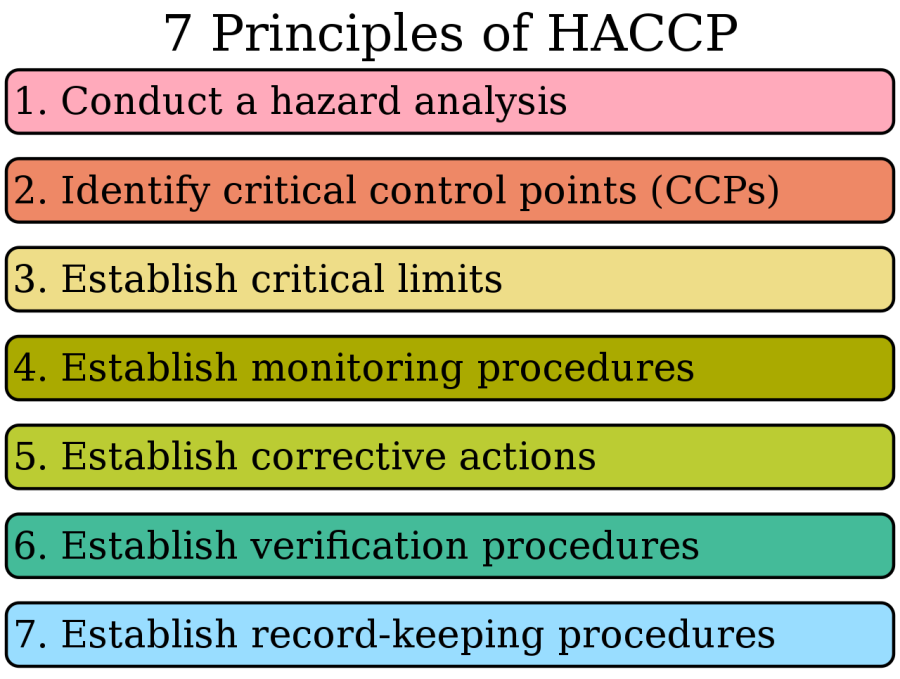
At its core, HACCP consists of seven principles that serve as a comprehensive framework for ensuring food safety:
- Hazard Analysis
- Identifying Critical Control Points (CCPs)
- Establishing Critical Limits
- Monitoring Procedures
- Corrective Actions
- Verification
- Record-Keeping and Documentation
Each of these principles serves a specific purpose in identifying and preventing potential hazards that could compromise the safety of the food being produced and consumed.
Implementing HACCP is not only a legal requirement in many countries but also a vital component of responsible food production. By adhering to the principles of HACCP, food establishments can demonstrate their commitment to providing safe and quality products to consumers.
The significance of HACCP in preventing foodborne illnesses cannot be overstated. By addressing potential hazards at each critical control point, businesses can implement effective control measures to eliminate or reduce the risk of contamination.
This systematic approach helps identify and mitigate risks, allowing for the production of safe and hygienic food.
Furthermore, HACCP systems provide a proactive and preventive approach to food safety rather than relying solely on end-product testing.
By implementing HACCP protocols, businesses can identify and address potential hazards before they become issues, ensuring that all stages of the food production process adhere to stringent safety standards.
The benefits of HACCP extend beyond consumer safety. By adopting HACCP practices, businesses can reduce the likelihood of costly product recalls, legal battles, and damage to their brand reputation.
Implementing HACCP protocols also helps businesses comply with regulatory requirements and fosters trust with both customers and stakeholders.
Real-World Examples
Several leading food establishments have successfully implemented HACCP systems to enhance food safety. Here are some notable examples:
| Company | Industry | Impacts of HACCP Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Walmart | Retail | Improved supply chain management, enhanced product quality, and reduced foodborne illnesses. |
| McDonald’s | Food Service | Enhanced food safety protocols, increased customer satisfaction, and strengthened brand reputation. |
| Nestlé | Food Manufacturing | Streamlined production processes, reduced risks of contamination, and ensured compliance with global food safety standards. |
The 7 Principles of HACCP for Ensuring Food Safety
In this subsection, we will explore the 7 principles of HACCP and how they play a vital role in maintaining food safety. Understanding these principles is essential for every food establishment to adhere to strict standards and protect consumers from foodborne illnesses.
1. Conduct a Hazard Analysis:
The first principle of HACCP involves identifying and assessing potential hazards at each stage of the food production process. This analysis helps in determining critical control points and implementing effective control measures to mitigate risks.
2. Determine Critical Control Points (CCPs):
Identifying CCPs is the next step in the HACCP process. CCPs are the crucial points in the production process where control measures can be applied to prevent, eliminate, or reduce potential hazards. These points are essential for ensuring that food safety risks are effectively controlled.
3. Establish Critical Limits:
Critical limits are the acceptable boundaries defined for each CCP. These limits represent the maximum or minimum values to which a parameter must be controlled to prevent food safety hazards. Establishing critical limits helps in maintaining consistent quality and safety throughout the production process.
4. Monitor CCPs:
Regular monitoring of CCPs is necessary to ensure that critical limits are being met consistently. Monitoring involves observing and recording data to verify that control measures are effective in preventing or reducing hazards. This process enables the proactive identification of any deviations from critical limits.
5. Establish Corrective Actions:
If a deviation from critical limits occurs, immediate corrective actions must be taken. Establishing corrective actions ensures that any potential hazards are addressed promptly to prevent unsafe food from entering the market.
These actions should be predefined and formulated based on the hazards identified in the hazard analysis.
6. Implement Verification Procedures:
Verification procedures are essential for validating the effectiveness of the HACCP system. These procedures include regular inspections, audits, and reviews to ensure that the established control measures are working as intended.
Verification helps in identifying any gaps or shortcomings in the system and taking necessary corrective actions.
7. Establish Documentation and Record Keeping:
Accurate and comprehensive documentation forms the backbone of an effective HACCP system. It includes hazard analysis, critical control points, critical limits, monitoring records, corrective actions, and verification procedures.
Documentation ensures that all steps and measurements are recorded, providing evidence of compliance with food safety regulations.
By adopting and implementing these 7 principles of HACCP, food establishments can create robust food safety systems that prioritize consumer health and well-being.
These principles help in preventing contamination, reducing the risk of foodborne diseases, and ensuring safe food practices.
Implementing HACCP: Best Practices and Challenges
Implementing Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) is a crucial step for ensuring food safety in any food establishment.
Setting up an Effective HACCP Plan
When implementing HACCP, it is essential to follow best practices to establish a robust and effective plan. Here are some key steps to consider:
- Conduct a thorough hazard analysis: Identify and assess potential hazards at each stage of the food production process.
- Determine critical control points (CCPs): Identify the critical points where control measures can be implemented to mitigate or eliminate hazards. These points should have measurable parameters for monitoring.
- Establish control limits: Define the acceptable limits for each critical control point to ensure food safety.
- Implement monitoring procedures: Develop protocols for regularly monitoring and documenting CCPs to ensure that they are under control.
- Set corrective actions: Define procedures to be implemented when a critical limit is exceeded. These actions should be effective in bringing the CCP back under control.
- Establish verification procedures: Develop methods to validate the effectiveness of the HACCP plan, including regular internal audits and external inspections.
- Maintain proper documentation: Document all aspects of the HACCP plan, including records of monitoring, corrective actions, and verification procedures.
Common Challenges Faced During Implementation
While implementing HACCP, businesses may encounter various challenges that need to be addressed effectively for a successful implementation. Some of the common challenges include:
- Resistance to change: Implementing HACCP often requires changes to existing processes and may meet initial resistance from staff. Effective communication and training programs can help overcome this challenge.
- Lack of resources: Allocating sufficient resources, such as time, manpower, and financial investment, can be a challenge for smaller businesses. Planning and budgeting are crucial for overcoming this obstacle.
- Complexity of documentation: Maintaining detailed records and documentation can be overwhelming and time-consuming. Streamlining documentation processes and implementing digital solutions can simplify this task.
- Continuous training and education: Keeping up with changing regulations, updates, and new best practices can be a challenge. Regular training and education programs ensure that staff remains knowledgeable and up-to-date.
- Monitoring and verification: Consistently monitoring CCPs and conducting regular verification procedures can be challenging. Utilizing technology-based monitoring systems can streamline these processes and provide real-time data.
“Implementing HACCP requires careful planning, commitment, and adherence to best practices. Overcoming challenges is an integral part of the process, ensuring that food establishments can maintain high standards of food safety.” – John Johnson, Food Safety Expert
| Challenge | Best Practice |
|---|---|
| Resistance to change | Effective communication and training programs |
| Lack of resources | Proper planning and budgeting |
| Complexity of documentation | Streamlining documentation processes, digital solutions |
| Continuous training and education | Regular training programs, staying updated with regulations |
| Monitoring and verification | Utilizing technology-based monitoring systems |
By following these best practices and addressing challenges proactively, businesses can successfully implement HACCP, ensuring the highest levels of food safety.
Training and Auditing for HACCP Compliance
Ensuring HACCP compliance requires more than just implementation. Proper training and regular auditing are vital components of a successful food safety program.
In this subsection, we will explore the training requirements for individuals involved in HACCP implementation, as well as the importance of conducting comprehensive audits.
Training for HACCP
Effective training equips individuals with the knowledge and skills necessary to implement and maintain HACCP principles.
Training programs should cover topics such as hazard analysis, critical control points, and corrective actions. Employees need to understand their roles and responsibilities in upholding food safety standards.
Organizations can provide training through various methods, such as in-person workshops, online courses, or a combination of both. Training should be tailored to the specific needs of the employees, considering their roles, responsibilities, and level of understanding.
By investing in thorough training, businesses can ensure that their staff possesses the necessary expertise to implement HACCP protocols effectively. This not only minimizes the risk of foodborne illnesses but also enhances customer trust and confidence.
HACCP Auditing
Regular audits are critical to assessing the effectiveness of HACCP systems and identifying areas for improvement. Auditing involves reviewing the entire food production process, from sourcing raw materials to final product distribution.
It helps to ensure that all critical control points are properly monitored and that corrective actions are taken promptly.
Internal audits, conducted by trained personnel within the organization, provide valuable insights into the company’s compliance with HACCP principles. These audits can be scheduled at regular intervals to evaluate ongoing adherence to food safety standards.
External audits, performed by independent third-party organizations or regulatory bodies, offer additional accountability and validation. These audits verify the effectiveness of the company’s HACCP system and provide external recognition of compliance.
Through comprehensive auditing, businesses can identify potential weaknesses in their food safety practices and make the necessary improvements. By continuously monitoring and evaluating their HACCP systems, organizations can uphold the highest standards of food safety and ensure regulatory compliance.
By prioritizing training and auditing, businesses can maintain HACCP compliance and safeguard the health and well-being of consumers.
The implementation of robust training programs and regular audits not only minimizes the risk of foodborne illnesses but also demonstrates a commitment to food safety standards.
With the proper knowledge and ongoing evaluation, businesses can establish themselves as leaders in the industry while ensuring the highest level of customer satisfaction and trust.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the 7 principles of HACCP play a crucial role in promoting food safety. By understanding and implementing these principles, businesses can ensure the well-being of their consumers by upholding safe consumption and handling practices.
This, in turn, significantly reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses and contributes to a healthier and safer environment for all.
HACCP principles are designed to identify potential hazards and establish critical control points to prevent or minimize their occurrence.
By adhering to these principles, businesses can effectively manage and control risks, ensuring the highest food safety standards are maintained.
The food industry needs to emphasize the significance of HACCP principles and prioritize their implementation.
This not only demonstrates a commitment to food safety but also establishes trust and confidence among consumers. By investing in comprehensive HACCP programs, businesses can protect their reputation and contribute to a safer food supply chain overall.
FAQ
What is HACCP and why is it important in food safety?
HACCP stands for Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points. It is a systematic approach to identifying, evaluating, and controlling food safety hazards.
HACCP is crucial in ensuring food safety as it helps prevent foodborne illnesses by establishing control measures at critical points in the food production process.
What are the 7 principles of HACCP?
The 7 principles of HACCP include hazard analysis, identifying critical control points, establishing critical limits, monitoring procedures, corrective actions, verification procedures, and record-keeping.
These principles work together to ensure that potential hazards are identified and controlled to maintain food safety.
How can HACCP be implemented effectively?
Implementing HACCP effectively involves developing a detailed plan, conducting a hazard analysis, identifying critical control points, establishing critical limits, implementing monitoring procedures, defining corrective actions, conducting regular verifications, and maintaining thorough record-keeping.
It is essential to follow best practices and address any challenges that may arise during the implementation process.
What are the training requirements for HACCP compliance?
Individuals involved in HACCP implementation should receive proper training on the principles and procedures.
This training should cover topics such as hazard analysis, critical control points, monitoring procedures, and corrective actions. It is important to ensure that all employees understand their roles in maintaining HACCP compliance and food safety.
Why is auditing necessary for HACCP compliance?
Auditing plays a crucial role in HACCP compliance by assessing the effectiveness of the implemented system.
Regular audits help identify any deficiencies or areas for improvement, ensuring that the HACCP plan is being followed correctly. Auditing also provides an opportunity to address any non-compliance issues and maintain consistent food safety standards.





